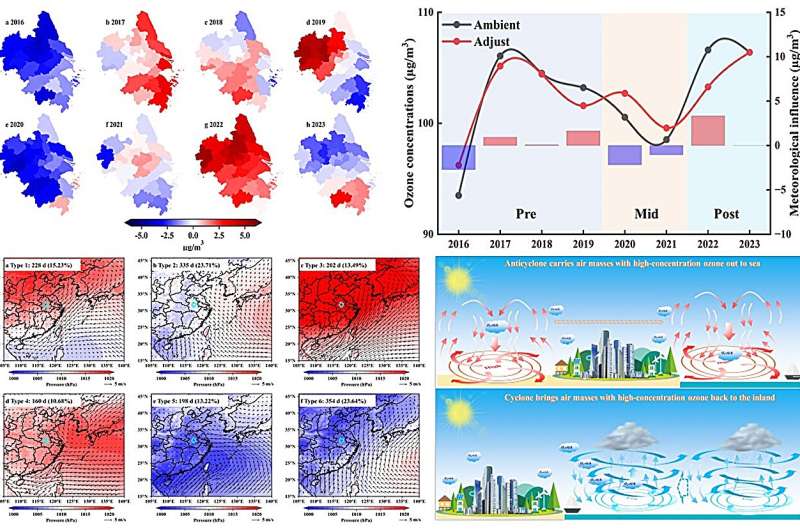
Figure: Interannual variations, synoptic classification of weather patterns and multiscale transport processes of ozone in the Yangtze River Delta. Image credit: HU Feng
A group of researchers identified key synoptic weather patterns (SWPs) associated with severe ground-level ozone pollution in the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) and determined the relationship between the evolution of these SWPs and persistent severe ozone pollution in terms of ozone formation and transport by analyzing the long-term ozone evolution in this area. The research team was led by Prof. Xie Pinhua from the Hefei Institute of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The results of their study were published in Science of the entire environmenttogether with two articles in Journal of Environmental Sciencesand offers potential solutions to prevent and control severe ozone pollution.
High concentrations of tropospheric ozone are a significant air pollutant in summer and pose a serious threat to human health and plant growth. In recent years, ozone concentrations in the YRD have shown fluctuating trends. However, their driving factors, multiscale transport processes and sources remain unclear.
In the study, based on data from multiple sources and numerical models, researchers found that changes in emissions are the main cause of recent fluctuations in ozone levels, with emissions causing ozone to increase during colder seasons.
They also found that the fringes of typhoons are among the main weather phenomena causing severe ground-level ozone pollution in Hefei, a central Chinese city. Moreover, these ozone sources are connected to southeastern transport routes.
In addition, research found that changing weather patterns such as cold fronts and typhoon circulation caused ozone to migrate from northern China into the YRD and then to the sea, where it eventually returned to land.
“These findings enable a deeper understanding of the meteorological mechanisms as well as the formation and transport processes of severe ozone pollution in the YRD,” said Prof. Xie.
Further information:
Feng Hu et al., The influence of evolving synoptic weather patterns on multiscale transport and sources of persistent high-concentration ozone pollution in the Yangtze River Delta, China, Science of the whole environment (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.175048
Feng Hu et al., Impacts of synoptic weather patterns on Hefei’s warm-season ozone and analysis of transport pathways during extreme pollution events, Journal of Environmental Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2024.06.032
Feng Hu et al., Long-term ozone trends in the Yangtze River Delta, China: Spatiotemporal effects of meteorological factors, local and non-local emissions, Journal of Environmental Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2024.07.017
Provided by the Chinese Academy of Sciences
Quote: Research helps better understand ozone pollution in the Yangtze River Delta (August 13, 2024), accessed August 13, 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-08-ozone-pollution-yangtze-river-delta.html
This document is subject to copyright. Except for the purposes of private study or research, no part of it may be reproduced without written permission. The contents are for information purposes only.

